It is often said that the pyramid of energy is always upright. On the other hand, the pyramid of biomass can be both upright and inverted. Explain with the help of examples and sketches.
The pyramid of energy represents the total amount of energy consumed by each trophic level in a given food chain. An energy pyramid is always upright because when energy flows from a particular trophic level to the next trophic level, some energy is always lost as heat at each step.
Thus the total amount of energy available for utilisation in the top levels is always less than the energy available in the lower levels. Therefore in the pyramid of energy in which each bar in the indicates the amount of energy present at each trophic level in a given time or annually per unit area is always upright as the higher trophic levels have lower energy. For example the energy available to the tertiary consumer level is lower than the energy available to the producer level.
The pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of the total amount of living matter present at each trophic level of an ecosystem. The pyramid of biomass can be both upright and inverted.
Upright pyramid of biomass is shown by grassland ecosystem. In this ecosystem, the number of biomass present at tertiary level is less than the secondary and the producer levels. For example, the biomass of plants that is grass is the highest followed by the biomass of mice and snake. The biomass of eagle which forms the tertiary consumer is the lowest.
Inverted pyramid of biomass - The pyramid of biomass is inverted in a pond ecosystem as the biomass of fishes exceeds the biomass of zooplankton (upon which they feed).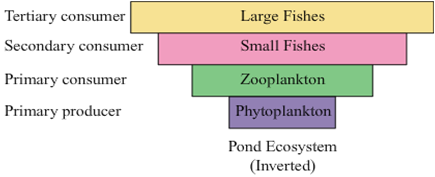
1. Plants are called as .......................because it fixes carbon dioxide.
2. In ecosystem, dominated by trees, the pyramid is.......................type.
3. In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is.......................
4. Common detritivores in our ecosystem are.......................
5. The major reservoir of carbon is.......................
Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Give an account of energy flow in an ecosystem.
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
(b) Production and decomposition
(c) Upright and inverted pyramid.
(d) Food chain and food web
(e) Litter and detritus
(f) Primary and secondary productivity.
Describe the advantages for keeping the ecosystems healthy.
Explain the carbon cycle with the help of a simplified model.
Explain how does:
(a) a primary succession start on a bare rock and reach a climax community?
(b) the algal bloom eventually choke the water body in an industrial area?(a) Explain primary productivity and the factors that influence it.
(b) Describe how do oxygen and chemical composition of detritus control decomposition?
(a) Explain the significance of ecological pyramids with the help of an example.
(b) Why are the pyramids referred to as upright or inverted?(a) Taking an example of a small pond explain how the four components of an ecosystem function as a unit.
(b) Name the type of food chain that exists in a pond.
Discuss the role of healthy ecosystem services as a prerequisite for a wide range of economic, environmental and aesthetic goods and services.