Explain the carbon cycle with the help of a simplified model.
Key process involved in carbon cycle is photosynthesis and respiration.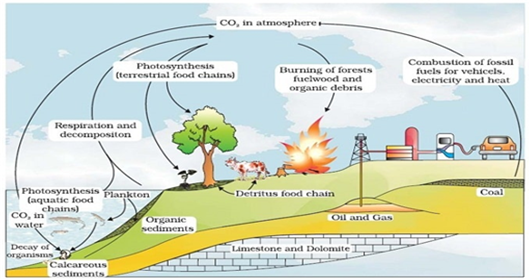
Carbon cycling occurs through atmosphere, ocean and through living and dead organisms.
1. Carbon is fixed during photosynthesis by the plants.
2. A large amount of carbon is returned to the atmosphere as CO2 by the respiratory activities of organisms.
3. Decomposers also contribute substantially to the CO2 by acting on waste materials and dead organic matters.
4. Some of the fixed carbon is lost to the sediments and removed from the circulation.
5. Burning of fossil fuels forest fire and combustion of organic matter volcanic activity also release CO2 in the atmosphere.
1. Plants are called as .......................because it fixes carbon dioxide.
2. In ecosystem, dominated by trees, the pyramid is.......................type.
3. In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is.......................
4. Common detritivores in our ecosystem are.......................
5. The major reservoir of carbon is.......................
Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Give an account of energy flow in an ecosystem.
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
(b) Production and decomposition
(c) Upright and inverted pyramid.
(d) Food chain and food web
(e) Litter and detritus
(f) Primary and secondary productivity.
Describe the advantages for keeping the ecosystems healthy.
Explain how does:
(a) a primary succession start on a bare rock and reach a climax community?
(b) the algal bloom eventually choke the water body in an industrial area?(a) Explain primary productivity and the factors that influence it.
(b) Describe how do oxygen and chemical composition of detritus control decomposition?
It is often said that the pyramid of energy is always upright. On the other hand, the pyramid of biomass can be both upright and inverted. Explain with the help of examples and sketches.
(a) Explain the significance of ecological pyramids with the help of an example.
(b) Why are the pyramids referred to as upright or inverted?(a) Taking an example of a small pond explain how the four components of an ecosystem function as a unit.
(b) Name the type of food chain that exists in a pond.
Discuss the role of healthy ecosystem services as a prerequisite for a wide range of economic, environmental and aesthetic goods and services.